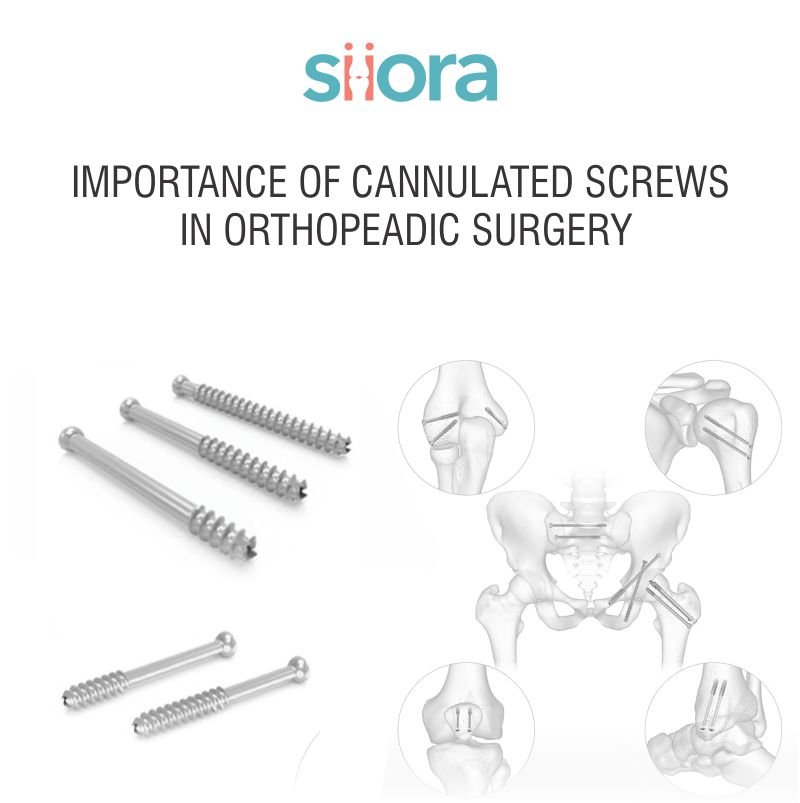
Orthopedic surgery has evolved dramatically over the years, driven by advancements in technology and innovative surgical techniques. One such revolutionary development in this field is the introduction of cannulated screws. These specialized screws play a pivotal role in the successful treatment of various bone injuries and deformities. Designed with a hollow core, cannulated screws provide several benefits, making them a preferred choice for surgeons worldwide. Let’s delve into the importance of cannulated screws in orthopedic surgery and how they contribute to improved patient outcomes.
What Are Cannulated Screws?
Cannulated screws are a type of orthopedic hardware characterized by their hollow center. This hollow channel allows surgeons to insert the screw over a guidewire, ensuring precise placement. The screws come in various sizes and designs, catering to different surgical needs and anatomical requirements.
The ability to use a guidewire significantly reduces the risk of misplacement, making cannulated screws especially valuable in complex procedures. These screws are primarily made of biocompatible materials such as stainless steel or titanium, ensuring durability and safety within the human body.
What Are the Applications of Cannulated Screws in Orthopedic Surgery?
Cannulated screws are versatile tools used in numerous orthopedic procedures. Some of the most common applications include:
Fixation of Fractures
Cannulated screws are widely used to stabilize fractures, particularly in areas where precise alignment is critical. Common examples include femoral neck fractures, scaphoid fractures, and fractures in small bones such as the wrist and ankle.
Treatment of Nonunions
In cases where bones fail to heal properly, cannulated screws can be used to provide stability and promote bone regeneration.
Arthrodesis Procedures
Cannulated screws are often employed in joint fusion surgeries, such as fusing the ankle or wrist joints to alleviate pain and improve stability.
Pediatric Orthopedics
Due to their precision, cannulated screws are ideal for treating fractures in children, where maintaining growth plate integrity is crucial.
Minimally Invasive Surgeries
Cannulated screws are a cornerstone of minimally invasive orthopedic procedures, reducing tissue damage and promoting quicker recovery.
What Are the Advantages and Importance of Cannulated Screws?
Cannulated screws offer several advantages over traditional screws, making them an indispensable part of modern orthopedic surgery:
Precision Placement
The use of a guidewire ensures that the screw is positioned accurately, reducing the risk of complications such as malalignment or penetration into unwanted areas.
Minimally Invasive Approach
With the aid of cannulated screws, surgeons can perform procedures with smaller incisions, leading to less postoperative pain, reduced scarring, and quicker recovery times for patients.
Versatility
Cannulated screws are available in a wide range of sizes and lengths, making them suitable for various bones and types of fractures.
Enhanced Stability
These screws provide robust fixation, which is essential for promoting proper bone healing and maintaining alignment during recovery.
Reduced Operative Time
The precision and ease of use associated with cannulated screws often lead to shorter surgical procedures, benefiting both patients and medical teams.
The Role of Imaging in Cannulated Screw Placement
A critical aspect of using cannulated screws is the reliance on imaging techniques such as fluoroscopy or X-rays. These imaging tools allow surgeons to visualize the guidewire and ensure accurate screw placement in real-time. This integration of imaging with surgical tools exemplifies how technology enhances the precision and safety of orthopedic procedures.
The Effectiveness of Cannulated Screws
Several studies and real-world cases have demonstrated the effectiveness and importance of cannulated screws in orthopedic surgery. For instance:
Femoral Neck Fractures
Cannulated screws have shown high success rates in stabilizing femoral neck fractures, particularly in younger patients. The precision of these screws minimizes complications and promotes faster healing.
Scaphoid Fractures
The use of cannulated screws in treating scaphoid fractures has led to improved union rates, reducing the likelihood of long-term complications such as arthritis.
Ankle Fractures
In cases of unstable ankle fractures, cannulated screws provide the necessary stability for proper healing while allowing for minimally invasive surgical techniques.
What Are the Challenges and Considerations in Using Cannulated Screws?
While cannulated screws offer numerous benefits, there are certain challenges and considerations associated with their use:
Technical Expertise
The use of guidewires and reliance on imaging require a high level of skill and experience from the surgical team.
Cost
Cannulated screws are typically more expensive than traditional screws, which may be a consideration in resource-limited settings.
Potential for Complications
Though rare, complications such as guidewire breakage or improper screw placement can occur if the procedure is not performed meticulously.
Future Innovations
The field of orthopedic surgery is continuously evolving, and cannulated screws are no exception. Ongoing research and development aim to further improve these devices, focusing on:
Biodegradable Materials
Efforts are being made to develop cannulated screws made from biodegradable materials that dissolve after the bone has healed, eliminating the need for removal surgery.
Smart Screws
Innovations in smart technology could lead to screws embedded with sensors to monitor healing progress and detect complications early.
Enhanced Imaging Integration
Advanced imaging techniques such as 3D navigation systems may provide even greater accuracy in screw placement.
Patient Perspectives
From a patient’s viewpoint, the use of cannulated screws often translates to less pain, smaller scars, and quicker returns to daily activities. Understanding the benefits and potential risks of these screws helps patients feel more informed and reassured about their treatment plans.
Conclusion
Cannulated screws have revolutionized the field of orthopedic surgery, offering unparalleled precision, stability, and versatility. Their role in treating fractures, nonunions, and joint disorders cannot be overstated. While challenges exist, the continued advancement of technology and surgical techniques promises to make these screws even more effective and accessible. By prioritizing patient outcomes and embracing innovation, cannulated screws are set to remain a cornerstone of orthopedic care for years to come.