Limb lengthening surgery is a highly specialized procedure aimed at correcting limb length discrepancies, deformities, or aiding in the treatment of certain congenital and post-traumatic conditions. A critical component of this surgery is the use of external fixators, which play an instrumental role in achieving desired outcomes. This blog explores what external fixators are, how they work, and their role in the limb lengthening process.
What are External Fixators?
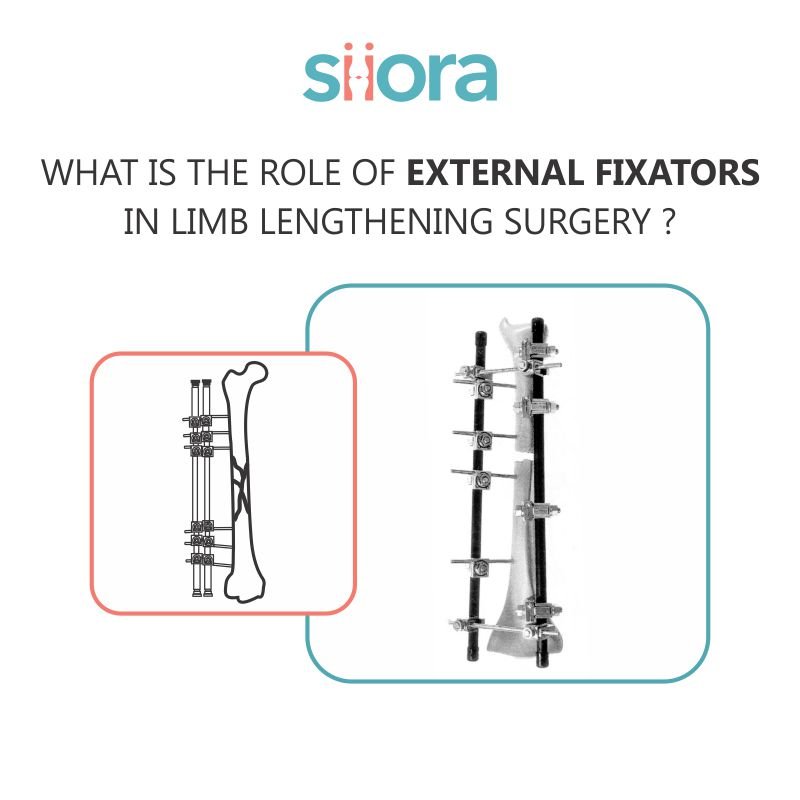
External fixators stabilize and support bones in orthopedic surgeries. Unlike internal fixators, which surgeons implant inside the body, external fixators stay outside the body and connect to the bone using pins or wires. These devices are adjustable and allow surgeons to make precise corrections over time.
External fixators are often used in:
- Limb lengthening procedures
- Correcting bone deformities
- Stabilizing fractures
- Treating complex orthopedic conditions such as nonunion fractures
The design of external fixators can vary depending on their application, but they typically consist of rings, rods, or frames that encircle the limb.
How Do External Fixators Work?
The principle behind external fixators in limb lengthening surgery lies in the body’s natural ability to heal and regenerate bone tissue. The process, known as distraction osteogenesis, involves cutting the bone (osteotomy) and gradually pulling the two segments apart using the external fixator. This controlled separation allows new bone to form in the gap, effectively increasing the length of the limb.
Here’s how the process unfolds:
Surgery
The surgeon makes an osteotomy to divide the bone. The external fixator is then attached to the limb, with pins or wires inserted into the bone segments.
Distraction Phase
After a short latency period to allow initial healing, the external fixator is adjusted daily to gradually separate the bone segments. This phase typically progresses at a rate of 1 mm per day.
Consolidation Phase
Once the desired length is achieved, the distraction stops, and the external fixator remains in place to allow the new bone to harden and fully integrate with the surrounding tissue.
Removal
The external fixator is removed once the bone has healed sufficiently.
What Are the Advantages of External Fixators in Limb Lengthening?
External fixators are indispensable in limb lengthening surgeries due to their versatility and precision. Some of their key benefits include:
Adjustability
External fixators can be fine-tuned during the distraction phase to ensure optimal alignment and length.
Minimally Invasive Application
While attaching the fixator involves surgery, the procedure is less invasive compared to some internal fixation techniques.
Versatility
These devices work for both simple and complex cases, including deformity corrections and simultaneous lengthening.
Encouraging Natural Healing
By leveraging the body’s regenerative capabilities, external fixators promote the growth of strong, healthy bone tissue.
What Are the Types of External Fixators?
There are several types of external fixators commonly used in limb lengthening surgeries:
Circular Fixators
These consist of rings and are often used for complex corrections. The Ilizarov frame is a well-known example.
Monolateral Fixators
These are single-sided devices that are more lightweight and simpler to use for straightforward cases.
Hexapod Fixators
Advanced fixators like the Taylor Spatial Frame use computer-aided adjustments to achieve precise corrections in multiple planes.
The choice of fixator depends on the specific needs of the patient and the complexity of the procedure.
What is the Role of External Fixators in Limb Lengthening?
External fixators are central to the success of limb lengthening surgeries. Their role extends beyond merely separating bone segments; they provide a framework for controlled growth and correction. Here’s a closer look at their functions:
Bone Stabilization
External fixators stabilize the bone during the lengthening process, ensuring that the segments remain aligned. This stability is crucial to prevent complications such as deformities or nonunion.
Controlled Distraction
The daily adjustments of the fixator allow for precise control over the rate and direction of bone growth. This control is vital for avoiding complications like over-lengthening or inadequate bone formation.
Soft Tissue Adaptation
As the bone lengthens, surrounding muscles, nerves, and blood vessels must stretch and adapt. External fixators facilitate gradual lengthening, giving soft tissues time to adjust and minimizing the risk of damage.
Correcting Deformities
In addition to lengthening, external fixators correct angular deformities or rotational issues, improving the overall functionality and appearance of the limb.
Challenges and Considerations
While external fixators offer numerous advantages, their use comes with challenges that patients and surgeons must address:
Infection Risk
The pins or wires inserted into the bone can serve as entry points for infection. Proper hygiene and regular follow-ups are essential to minimize this risk.
Patient Discomfort
Wearing an external fixator can be uncomfortable and may limit mobility. Physical therapy and pain management strategies can help.
Lengthy Treatment Period
The entire process, from surgery to fixator removal, can take several months. Patience and commitment are crucial for both patients and caregivers.
Complexity of Adjustments
In some cases, precise adjustments require technical expertise and may involve computer-aided planning.
Advancements in External Fixator Technology
Modern advancements have made external fixators more efficient and patient-friendly. Some of these innovations include:
Lightweight Materials
Newer fixators use lighter materials like titanium, which improve patient comfort..
Computer-Assisted Adjustments
Systems like the Taylor Spatial Frame enable surgeons to plan and execute corrections with greater precision.
Hybrid Fixators
Combining features of external fixation for fractures and internal fixation, hybrid systems offer enhanced stability and reduced treatment times.
Preparing for Limb Lengthening Surgery
For patients undergoing limb lengthening surgery with external fixators, preparation is key. Preoperative steps include:
Medical Evaluation
Comprehensive health assessments help ensure the patient’s fitness for surgery.
Education
Understanding the process, risks, and expected outcomes helps patients and their families prepare mentally and emotionally.
Physical Therapy
Pre-surgery exercises can strengthen muscles and improve recovery.
Postoperative Care
Recovery from limb lengthening surgery involves careful monitoring and adherence to postoperative guidelines. Key aspects include:
Pin Site Care
Regular cleaning of pin sites reduces infection risk.
Physical Therapy
Exercises to maintain joint mobility and muscle strength are crucial.
Follow-Up Appointments
Regular check-ups allow the surgeon to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments.
Emotional Support
The lengthy recovery process can be mentally taxing, making emotional and psychological support vital.
Conclusion
External fixators are a cornerstone of limb lengthening surgery, offering unmatched precision and versatility. By facilitating controlled bone growth and supporting soft tissue adaptation, lengthening fixators help patients achieve improved mobility and quality of life. Despite the challenges associated with their use, advancements in technology continue to enhance their efficiency and patient experience.
For individuals considering limb lengthening surgery, understanding the role of external fixators is an important step toward informed decision-making. With proper care and commitment, these devices can transform lives, enabling patients to overcome physical limitations and embrace a brighter future.