The field of orthopedics is ever-growing and if we talk about orthopedic implants, then they are much improved now that those decades ago. Orthopedic plates are among the oldest implants. The first successful plate was made in 1886 using nickel sheets. Since then, the trauma plates have seen a massive change. However, orthopedic plates that surgeons use now are way better and have good success rates. Nowadays, different types of plates are available that surgeons use for specific purposes.
This article will focus on discussing some details about orthopedic plates along with their types and uses. Let us start with a brief introduction to trauma plates.
What Are Orthopedic Plates?
Orthopedic plates are medical devices that orthopedic specialists use to treat fractures. These implants are not used alone as orthopedic screws are often required to fix them in a specific position. These plates hold the fracture in correct alignment and support the body in healing. They are the form of internal fixation devices that specialists use more often to fix a fracture. Above all, different types of these implants are there and surgeons choose them depending on the pattern, severity, and location of the fracture.
Besides fracture fixation, plates solve several other purposes in the orthopedic industry and their use is at many anatomic locations. Now, if we talk about the functions of orthopedic plates, then they differ depending on their types. Let us see the types of orthopedic plates along with their functions.
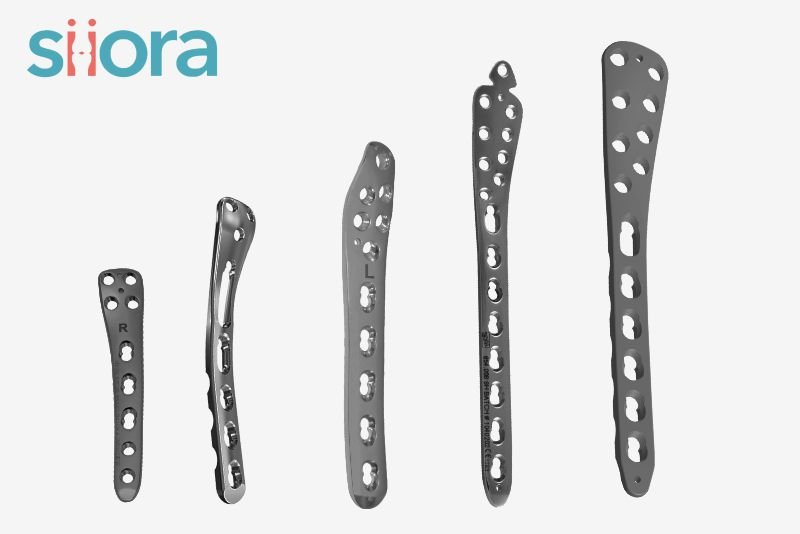

What Are the Types of Orthopedic Plates?
If we talk about the types of orthopedic plates, then they are classified based on their structure and function. Let us see them one by one.
Based on Structure
Trauma plates are available in different shapes and sizes based on the structure of different bones in our bodies. If we talk about the structure, we can broadly categorize orthopedic plates into 3 types:
Dynamic Compression Plate (DCP)
DCP exert dynamic pressure between broken bone fragments, this helps transfix the fracture while eliminating the chances of any movement of the fragments. A dynamic compression plate is a standard plate that works to bring the ends of broken bones together. Thus, this helps with better and faster healing of the fracture.
DCP plates are applied with orthopedic screws and when they are tightened, the force exerted moves the plate along the bone. Hence, this creates a dynamic force and ensures proper fixation & healing of the fracture. In most cases, the plates are applied on both sides of the fracture and the force exerted brings broken edges together.
Limited Contact Dynamic Compression Plate (LC-DCP)
The limited contact dynamic compression plates have the same use as of DCP plates. But they are advantageous when compared to DCP plates. LC-DCP orthopedic plates minimize vascular damage to the fractured bone. This happens because the plate applies less pressure on the bone when applied. Hence, there is less damage to the pericytes. Thus, the use of these plates ensures better healing of the fracture along with the blood flow.
Locking Compression Plate (LCP)
As we have said above the design of orthopedic plates has improved a lot and advanced ones are being used these days. A locking compression plate (LCP) is an advanced form of trauma plate that orthopedic surgeons use these days. LCP plates have combi-holes. This means they can accommodate both locking and standard (cortical) screws. These trauma plates are also suitable to create a fixed-angle construct which is not possible with standard plates.
The application of these plates reduces the plate-to-bone contact and this helps improve periosteum blood circulation. LCPs have a series of combination holes and this gives the liberty to the orthopedic surgeon to use the hole that fixes the fracture the best.
Based on Function
Different types of fractures require different types of trauma plates for treatment. Here are the types of plates that orthopedic specialists use for different purposes:
Buttress Plates
Buttress plates are orthopedic devices for the treatment of articular fractures. They support intraarticular fragments and orthopedic specialists apply them in the metaphyseal area.
Buttress plates have the unique function of bringing together fractures at the ends of long bones. These orthopedic plates move with the body part. Hence, they are best for use in areas like knees and ankles. These fracture sites experience a huge compression force. They also help prevent the sliding/shortening of broken bone fragments. As a result of their unique function, orthopedic specialists also call these plates as peri-articular plates. Buttress plates are available in T and L shapes.
Neutralization Plates
Neutralization plates distributes the load around the bone’s length evenly. In other words, these plates remove loading forces from the fracture site. However, the use of these plates helps the orthopedic surgeon fix the fracture using other implants. These plates can provide added protection and support to the fracture.
Neutralization plates do not have any special design. Their key function is to hold fractured bone fragments together and provides resistance against compression and torsional forces. Besides this, these plates have a protective function. The lag screws prevent neutralization plates from bending and rotating.
Tension Plates
They are used on fractures that have occurred from eccentric loading forces. Orthopedic specialists apply these plates on the tension side of the fracture to convert tension forces into compression forces. The application of tension plates helps broken bones withstand distraction forces by transforming tensile forces into compression forces. Hence, tension plates have a protective function for the fractured site.
Bridging Plates
Orthopedic bridging plates are for the treatment of multi-fragmented or comminuted fractures. These plates join broken bone fragments by creating a bridge over them. Bridging plates prevent the dislocation of bone fragments by creating stability. This also helps minimize the risk of limb deformity. Another key role of bridging plates is to preserve bone supply to the fracture while assisting in faster & better healing.
Tubular Plates
Tubular plates are more than 1mm thick and are best for use in areas with low soft tissue. One disadvantage of these plates is that they have the less stabilizing ability when compared to other plates.
Reconstruction Plates
The orthopedic surgeon can bend reconstruction plates as required to match the anatomy of the fractured bone using a plate bender for reconstruction plates. The commonest use of these plates is to fix fractures in locations with complex 3-dimensional geometry like distal Humerus and pelvis.
Note – Technical expertise is important for correct bending of reconstruction plates as repeated contouring may make the plate weak.
What Orthopedic Plates Are Made of?
Orthopedic plates are made using different types of medical-grade metals and non-metals. The common materials that are used to manufacture them include:
- Stainless steel
- Titanium
- Cobalt-based alloys
- Polymers
- Bio-ceramics
Siora Surgicals Pvt. Ltd. is a renowned manufacturer of different types of orthopedic plates and other CE-certified implants. The company uses medical-grade stainless steel and titanium to manufacture implants. Siora owns a huge inventory of finished and semi-finished orthopedic devices. It serves around 130 national and international distributors and orthopedic surgeons and has served clients in over 40 countries. Siora is also among the leading OEM/contract manufacturing service providers across the globe.